Corrective and Preventive Actions in Food Safety and Sanitation Management
Introduction
In the highly regulated world of food production, safety and compliance are non-negotiable. Food businesses must be equipped to detect, correct, and prevent issues before they impact consumer health or disrupt operations. This is where Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) come into play. A structured approach that enhances accountability, reduces risk, and strengthens food safety programs.
In this article, we’ll break down what CAPA means in the context of food safety, why it matters, and how a digital Corrective and Preventive Actions module within your sanitation management software can improve operational excellence.
What is CAPA?
CAPA stands for Corrective and Preventive Actions. It is a systematic process used to investigate, solve, and prevent recurring problems in quality and safety systems.
- Corrective Action focuses on identifying and eliminating the root cause of an existing non-conformance or incident.
- Preventive Action focuses on detecting potential risks and taking proactive steps to avoid future problems.
In food safety, Corrective and Preventive Actions is critical for ensuring that any deviation from standard practices—whether due to contamination, equipment malfunction, or human error—is properly documented, addressed, and prevented from happening again.
Why CAPA is Essential in Food Safety Management
- Compliance with Regulations
Food manufacturers must meet standards set by regulatory bodies like FDA, EFSA, and GFSI-certified schemes (e.g., BRC, IFS, FSSC 22000). Corrective and Preventive Actions documentation is often reviewed during audits and inspections. - Continuous Improvement
Corrective and Preventive Actions promotes a culture of learning and improvement, helping teams enhance hygiene protocols, sanitation effectiveness, and quality control procedures. - Risk Mitigation
By addressing root causes and implementing preventive strategies, businesses can reduce downtime, avoid product recalls, and protect consumer health. - Audit Readiness
Having a digital CAPA process ensures full traceability and readiness for internal and external audits.
Common Triggers for CAPA in Food Production
- Failed microbiological or allergen test results
- Sanitation verification failures
- Equipment breakdowns or calibration errors
- Foreign body contamination
- Staff non-compliance with SOPs
- Customer complaints or product returns
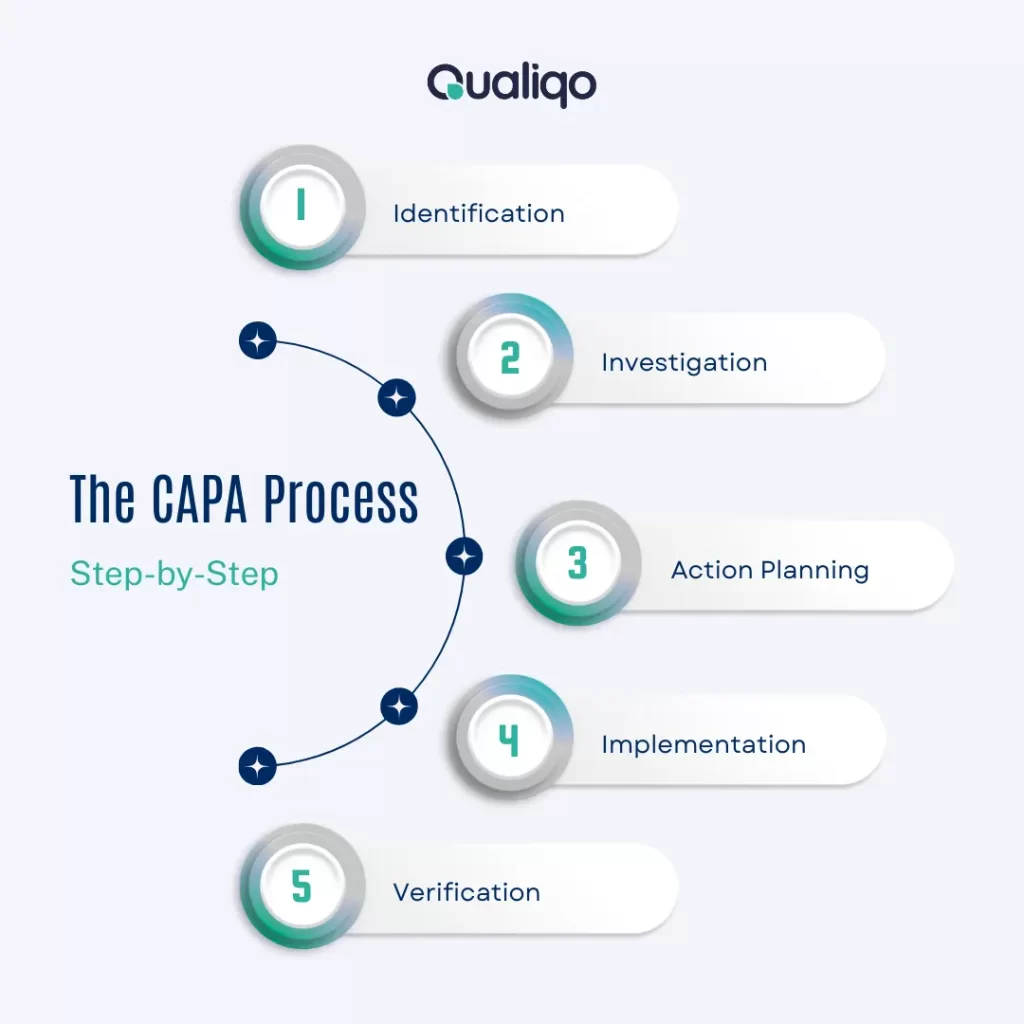
The CAPA Process: Step-by-Step
1. Identification
Record the non-conformance or risk through your digital sanitation management system.
2. Investigation
Conduct a RCA using the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram to determine the underlying cause.
3. Action Planning
Develop corrective and/or preventive measures tailored to the identified root cause.
4. Implementation
Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and apply the proposed actions using your digital workflow system.
5. Verification
Confirm that the action has resolved the issue. And that the same problem does not recur.
Benefits of a Digital CAPA Module in Your Sanitation Management System
A manual approach to CAPA can be time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to manage across teams and shifts. A digitally integrated Corrective and Preventive Actions module offers the following advantages:
Automated alerts and notifications to ensure timely follow-ups
Root cause analysis tools built into the system
Audit-ready documentation with time stamps and user tracking
Integration with other modules like Sanitation, Quality, and Pest Control
Real-time monitoring and dashboards for tracking recurring issues
CAPA as a Driver of Digital Transformation in Food Safety
In a modern food production environment, digital transformation is a competitive necessity. Embedding CAPA functionality empowers teams to respond swiftly and prevent incidents.
It also helps demonstrate compliance with confidence.
Adopting automated CAPA improves hygiene and safety outcomes. It also boosts operational efficiency and team accountability.
CAPA is more than just a regulatory requirement. It’s a foundational element of a robust food safety culture. By leveraging digital tools and workflows, food companies can transform CAPA from a reactive process into a proactive engine of continuous improvement.
If your business is ready to strengthen its safety program, reduce contamination risks, and optimize sanitation workflows, it’s time to explore a software solution designed with built-in CAPA capabilities.
Next Steps
Did you get enough information about “What is CAPA?”
Qualiqo is here to help you. It answers your questions about sanitation and hygiene, Lab. & EMP, IPM and Pest Control. We also provide information about the main features and benefits of the software. We help you access the Qualiqo demo and even get a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
CAPA stands for Corrective and Preventive Actions. It is a structured process used to identify, investigate, correct, and prevent problems that affect food safety, sanitation, or product quality.
CAPA ensures regulatory compliance, supports audit readiness, and helps maintain high food safety standards by continuously improving processes and preventing recurring issues.
Corrective action addresses the root cause of a known issue that has already occurred. Preventive action focuses on identifying and mitigating potential risks before they lead to a problem.